



| 2023/09/20 | Research by Yoshiki Tabuchi (M1) has been accepted in Acta Astronautica Journal. It is the world's first study on the permeability and freeze-thaw effects of lunar regolith layers. |
| 2023/09/01 | Associate Professor Kosuke Egawa has joined our team. |
| 2023/07/26 | Research by Natsuki Yamamoto (M1) has been accepted in Results in Surfaces and Interfaces Journal. It explores the adhesion inhibition and polymorphism of calcium carbonate crystals using wear-resistant zinc oxide silicone composites. |
| 2022/04/24 | Research by Yuya Komori (formerly M2) has been accepted in Renewable Energy Focus Journal. He proposed a simple sociophysical model on the social acceptance of renewable energy. |
| 2023/04/07 | We welcome 5 new M1 students and 5 new B4 students to our research group! |
| 2023/03/20 | Congratulations to all our graduates and alumni! |
| 2023/01/19 | We have updated our photo album. |
| 2022/05/31 | Takumu Nakamura (M1) has been awarded the "2022 Fukada Field Survey Grant." Congratulations! |
| 2022/05/31 | Research by Takeshi Tagomori (formerly M2) has been accepted in Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects Journal. It is the world's first study reporting the use of nanobubbles to inhibit crystal growth. |
| 2022/05/09 | We have revamped our website. |
The Earth has many untapped resources such as mantle and seabed resources. Our research focuses on these resources and renewable energy in line with the SDGs.

One method of measuring the strength of a rock mass is to use a test specimen, such as a uniaxial compression test. In a uniaxial compression test, the rock must be fractured and the core removed. Our research aims to estimate the strength of a rock mass nondestructively by using remote sensing techniques such as drones to quantitatively evaluate the degree of unevenness of the rock mass.

Nanobubbles (NB) are microscopic bubbles less than 1 µm in diameter, colorless, transparent, and not visible to the naked eye. Various studies are currently being conducted on nanobubbles, but there are still many unanswered questions. However, due to their high potential, they are expected to be applied in various fields such as agriculture, cosmetics, and drilling.
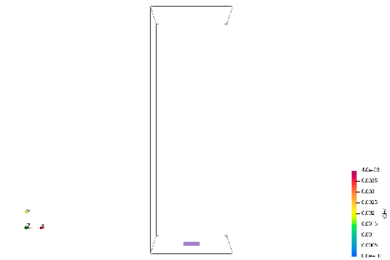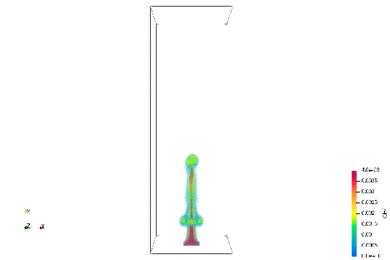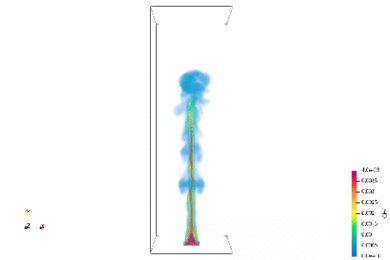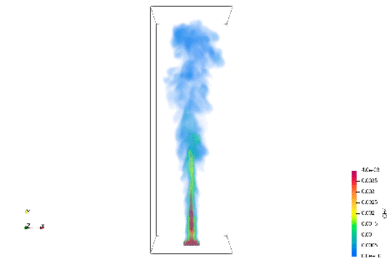
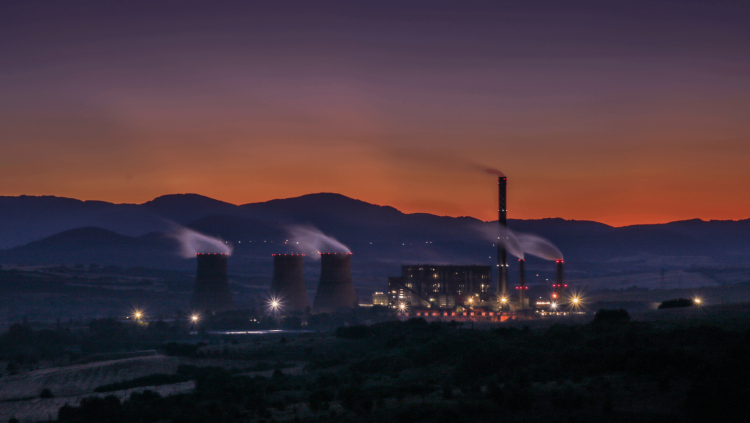
Spoil tip, accumulation sites for low-rank coal, are distributed throughout the world. Fires are currently causing problems in the mound interior. The methane and hydrogen sulfide emitted by the fires in the mounds are having a negative impact on the local population. We are studying the possibility of utilizing the methane and heat sources emitted from the mound as a resource through combustion analysis and InSAR.
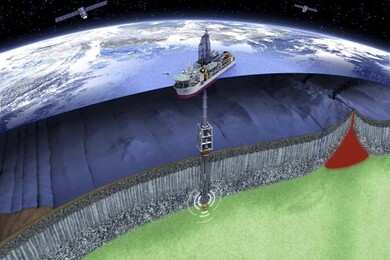
The mantle is located inside the crust of a planet, outside the core, and is hot and pressurized. Furthermore, hydrogen and helium are mainly contained in the mantle. In our laboratory, we are conducting research to extract and effectively utilize the hydrogen and helium in the mantle.

Japan is one of the world's leading countries in terms of geothermal resources. Our laboratory conducts research on geothermal energy in a wide range of areas, from underground geothermal reservoirs to aboveground geothermal power plants and direct geothermal utilization.

Methane hydrate is a substance formed when methane gas, the main component of natural gas and an energy resource, combines with water molecules. It is also called "flammable ice" because it burns when fire is brought close to it. Compared to oil and coal, methane emits half the amount of carbon dioxide when burned, and is therefore expected to be an effective new energy source as a countermeasure against global warming.

The physical properties of regolith are known to be very different from those of sand on Earth. Therefore, it is believed that the study of regolith is the key to future lunar activities and the acquisition of lunar resources.
Energy Resources Engineering Laboratory
〒819-0395
744 Motooka, Nishi-ku, Fukuoka City, Fukuoka Prefecture
Kyushu Univ. Room 418, West Bldg. 2, Ito Campus
